Is the Dining Chair ergonomic and comfortable to sit on for long periods of time?
Posted by Zhejiang Wanchang Furniture Co., Ltd.
An ergonomically designed Dining Chair can provide a comfortable sitting experience for a long time, but it must meet the core elements of structural adaptability, support, material and adjustability. The following is a specific analysis:
1. Core requirements of ergonomic design
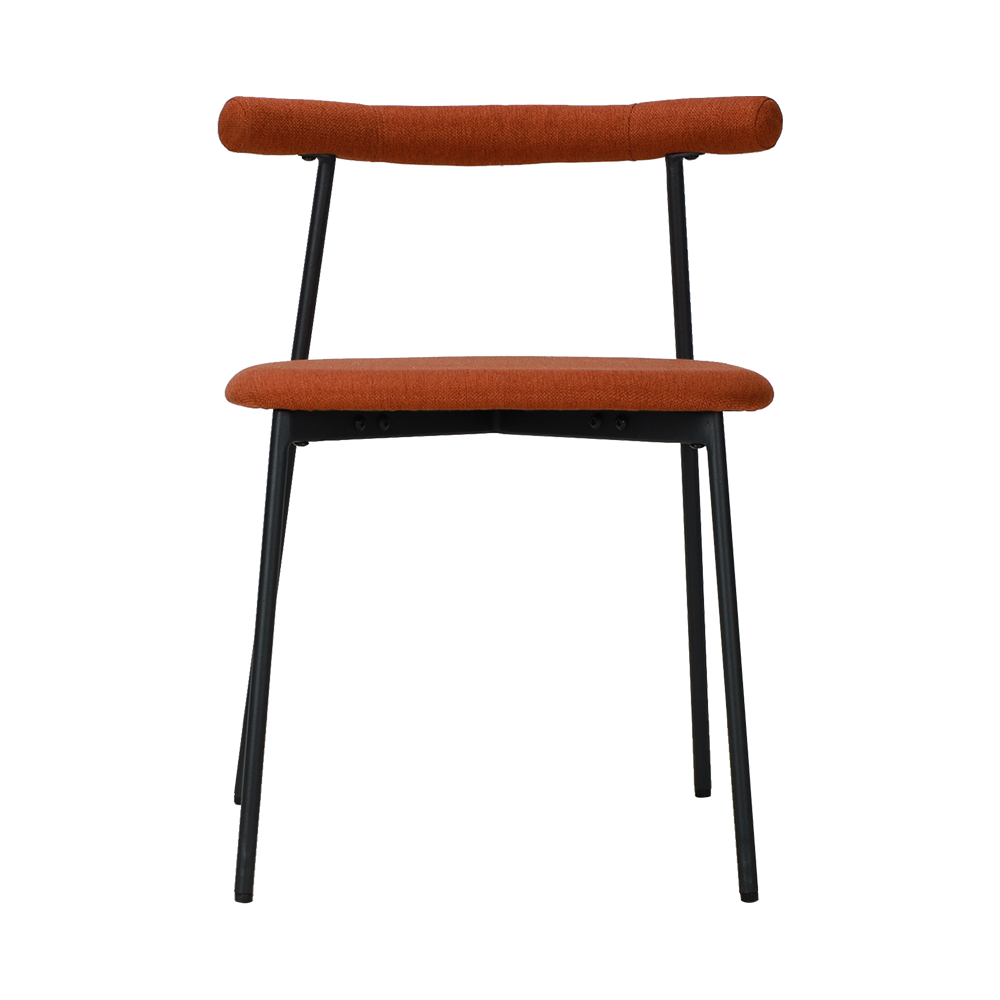
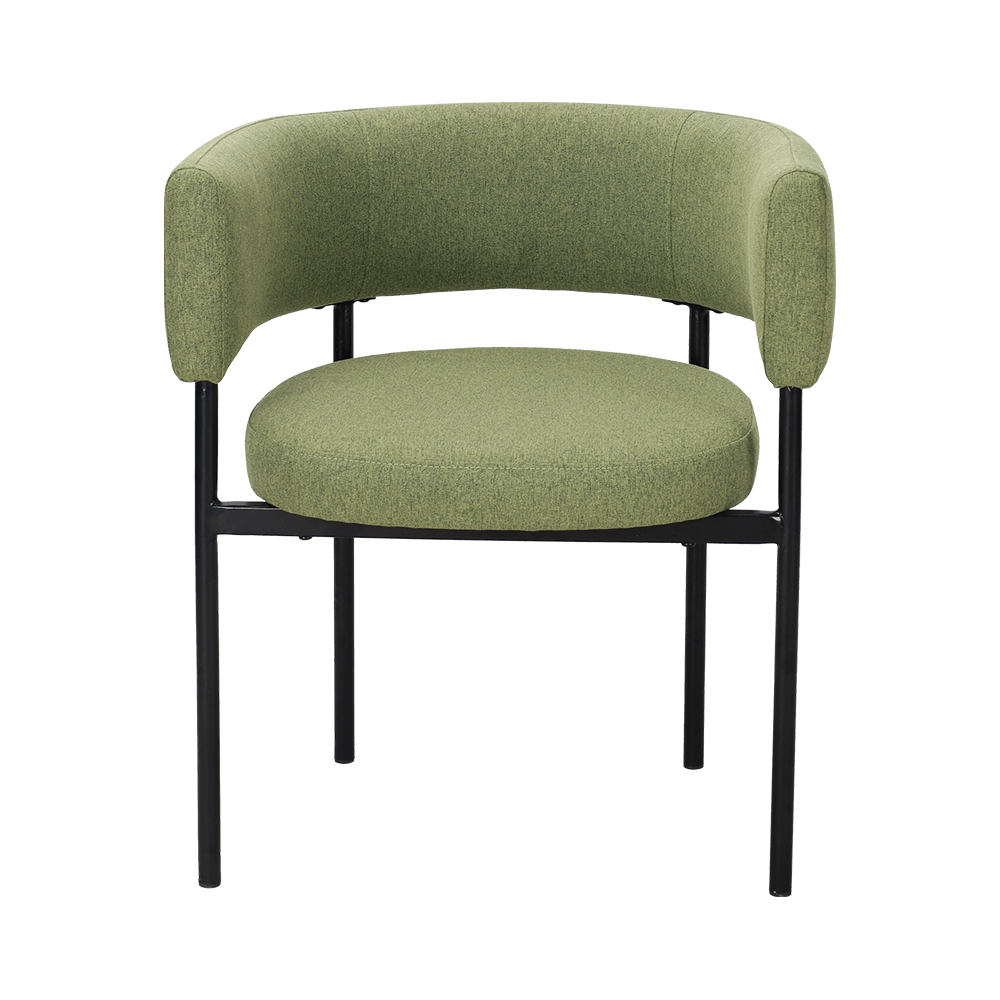
Sitting posture adaptability: The chair back needs to provide a tilt angle of 100°-110° to fit the natural spine curve of the human body and avoid excessive forward or backward leaning of the spine. For example, the curved backrest of the Baxter Corinne dining chair can reduce the feeling of waist suspension and reduce fatigue from sitting for a long time.
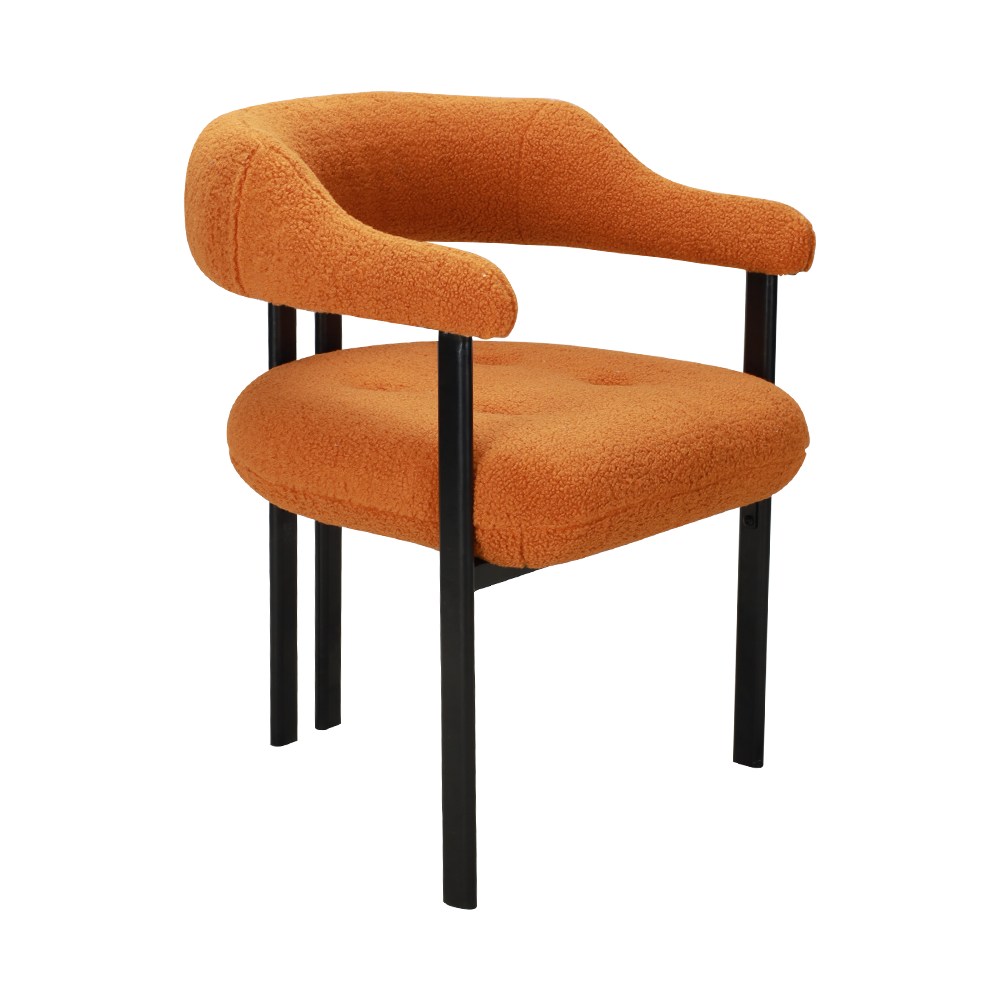
Support: The seat cushion needs to be made of high-density sponge (such as 40-50kg/m³) or latex material to disperse the pressure on the buttocks; the chair back needs to cover the waist to the shoulder blade area and provide S-shaped curve support, such as the leather backrest of the Visionnaire Sybilla Dining Chair, which can relieve back muscle tension.
Size adaptation: The seat height is recommended to be 42-45cm (dining table height-28-30cm), and the seat depth is 42-45cm to ensure that the legs droop naturally and the knees are not oppressed.

2. Influence of materials and craftsmanship
Breathability: Fabric or mesh materials (such as 3D breathable mesh) can improve the comfort of long-term use and avoid stuffiness; leather materials need to be matched with perforated design to enhance heat dissipation.
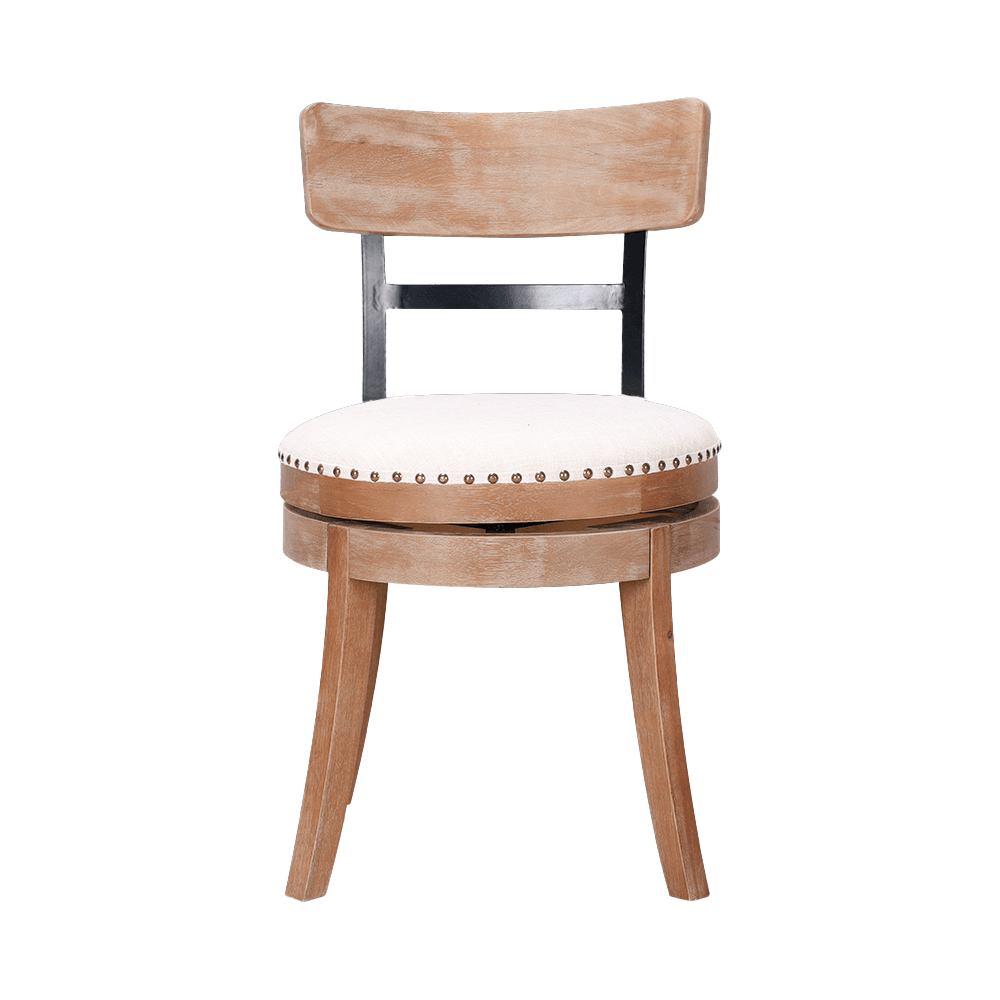
Structural stability: The chair legs need to be made of solid wood (such as ash wood) or metal frames (such as aluminum alloy), and the load-bearing capacity (recommended load-bearing ≥120kg) should be improved through triangular reinforcement or five-star foot design to avoid shaking after sitting for a long time.
3. Adjustability and adaptability
Dynamic adjustment: High-end dining chairs (such as some ergonomic office chair derivatives) can be equipped with air pressure lifting function, allowing users to adjust the seat height according to their height; the backrest tilt angle adjustment (such as 15°-20° range) can adapt to different sitting posture requirements.
Body adaptation: Wide seats (seat width ≥48cm) and thickened cushions (thickness ≥8cm) are suitable for larger people, while lightweight designs (such as Baxter Corinne dining chairs) are more suitable for small and medium-sized households.
4. Potential problems and improvement directions
Limitations of non-customized dining chairs: Standard-sized dining chairs may not be fully suitable for all body types (such as tall users need to raise the seat cushion).
Material aging: Poor-quality sponge or leather is prone to collapse. It is recommended to choose products with a warranty period of ≥3 years and regularly check the tightness of the chair leg screws.




 中文简体
中文简体 English
English